Site of the Gleaners who think that the universe is a spherical surface in at least four-dimensional space
5. Historical maybe last meeting of the Gleaners: The Doppler shift pattern in the closed universe --- It might have been
proved already<to the revised part>
Glass Snake:
We mentioned the dipole anisotropy of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) in the fourth meeting. It is an effect of the Doppler
shift caused by relative movement between the earth and the source of CMB (or the earthfs conjugate point).
There
are two types of Doppler shift in CMB. One type is caused by the expansion of
the universe, and its effect is isotropic. The type determines the average
value of Z parameter of CMB, and it must be treated by using relativistic
method. Here we are concerned about the other type caused by the relative
movement except the expansion of the universe. If the universe is open or flat,
there must be only the dipole anisotropy. However other anisotropies are
observed in CMB.
Robot: In my knowledge there are quadrupole and octupole anisotropies (low order anisotropies) and other higher order anisotropies, and the power of low order anisotropies is about 0.1-1% of that of the dipole.
Glass Snake: Since the closed universe of which model we have presented in the previous meetings has unique optical properties as discussed before, the effect of the Doppler shift in the closed universe may be different from that in an open universe.
Robot: The subject of this meeting is to discuss the Doppler shift pattern in the closed universe.
Glass Snake: Firstly, S. Pony, why don't you review the Doppler shift pattern in an open universe?
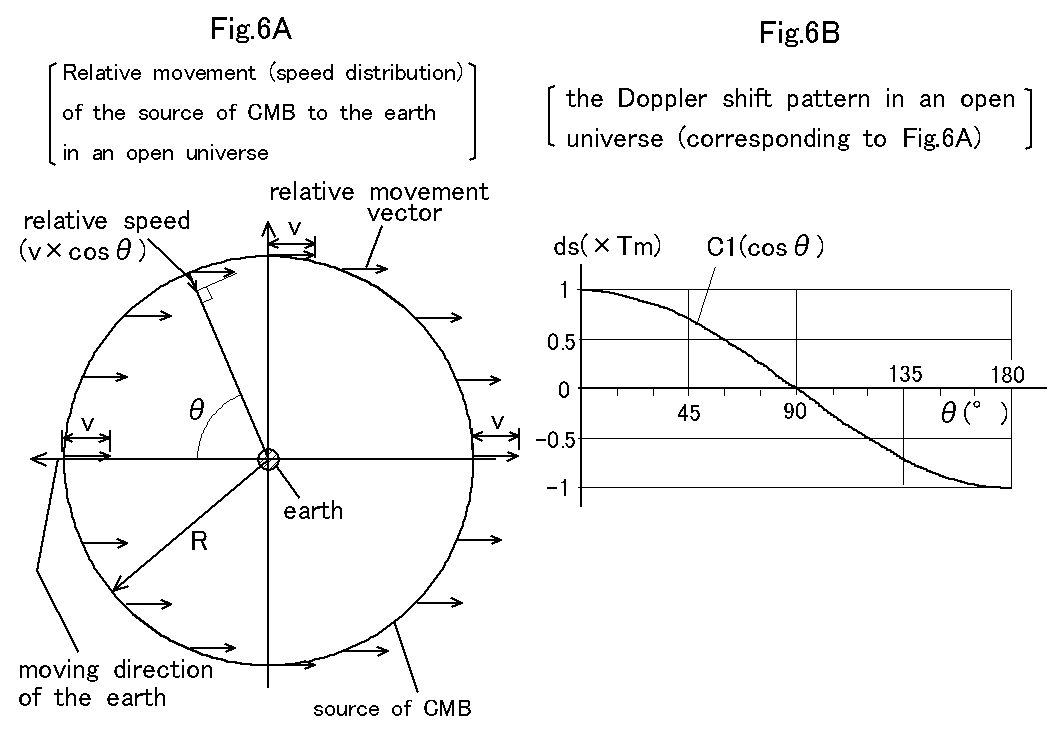
Stamp Pony: Let us suppose that the source of CMB in an open universe is a sphere of radius R where R is about the size (nearly 14 billion light years) of the universe as shown in Fig.6A, and the earth is moving at speed v to the source in a direction. Then the relative movement vector of the source to the earth is uniformly -v, and the relative speed of the source to the earth is v multiplied by cosฦ, where ฦ is an angle of the observing direction to the moving direction of the earth. Thus the Doppler shift pattern of the source in the open universe will be curve C1 as shown in Fig. 6B, where the value of curve C1 is cosฦ (normalized by the maximum value Tm(K)). We used a non-relativistic approximation.
Glass Snake: Secondly, P. Sheep, it's your turn to explain the Doppler shift pattern in the closed universe by using a non-relativistic approximation as you ate much at the sushi bar.
Puzzle Sheep: Let us suppose that the source of CMB in the closed universe is a sphere with radius r whose center is at the conjugate point C of the earth, where r is about one thousandth of the size of the universe as shown in Fig. 7A, and the earth is moving at speed v to the source along the prime meridian PM. And we introduce an equivalent source of CMB as shown in Fig. 7B, the equivalent source is an image observed from the earth as the real source, and the equivalent source is a sphere with radius r whose center is at the earth.
Then the relative movement vector of the equivalent source to the earth will become a tornado-like pattern. When the angle ฦ changes from 0 deg to 180 deg, the relative movement vector will rotate through 360 deg around the earth. Further when the angle ฦ changes from 0 deg to 90 deg or from 180 deg to 90 deg, the absolute value of the relative movement vector will decrease gradually. In this case since radius r is about one thousandth of the size of the universe, the absolute value sp1 of the relative movement vector at angle 45 deg or 135 deg is smaller than v by about 0.1 %, and the absolute value sp2 of the relative movement vector at angle 90 deg is smaller than v by about 0.2 %. The relative movement vector of the equivalent source is miller reflection of the relative movement vector of the real source to the conjugate point C in the radius direction.
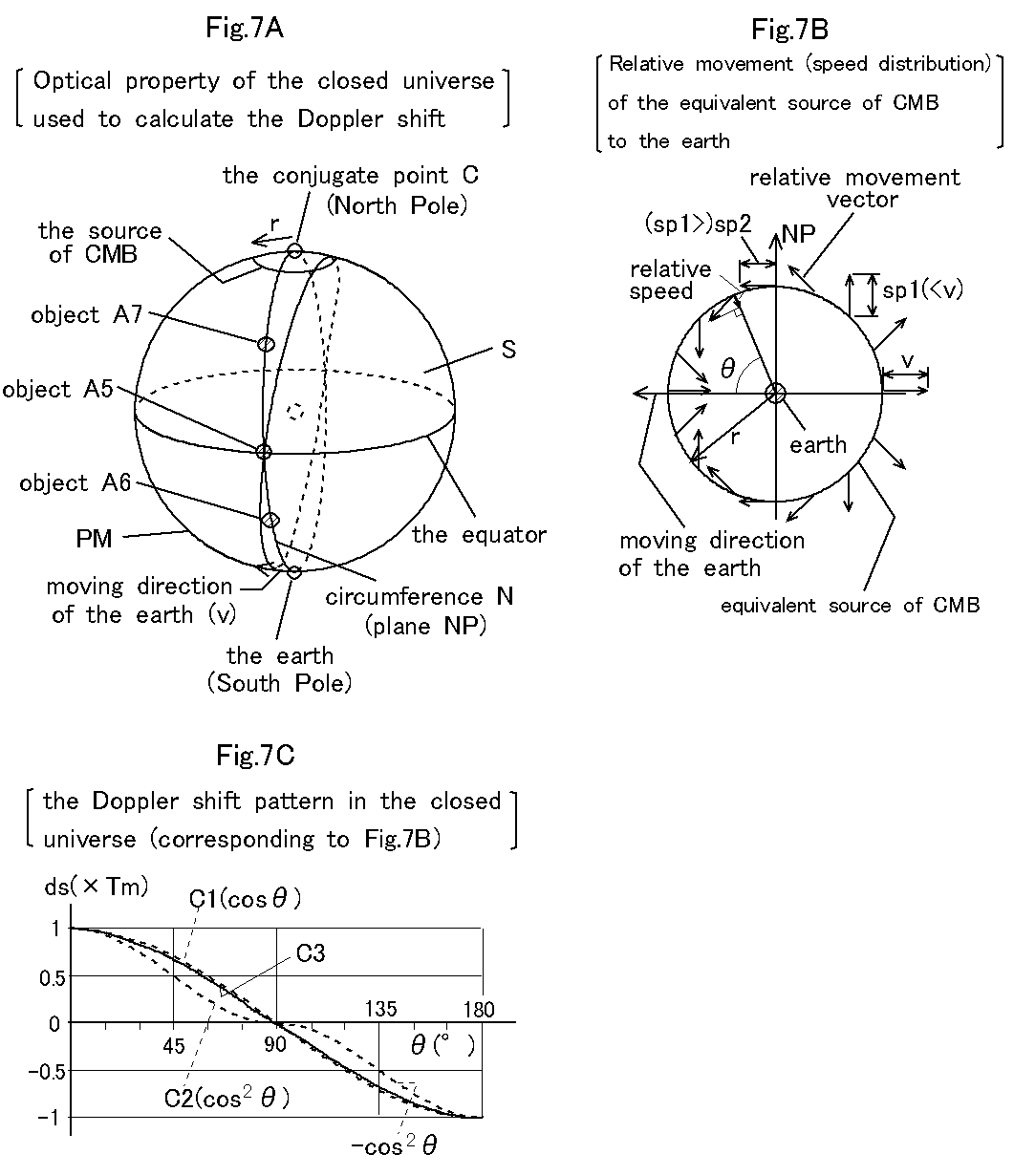
Although the relative movement vector in the closed universe (Fig. 7B) differs considerably from that in an open universe (Fig. 6A), the normalized Doppler shift pattern of the equivalent source in the closed universe will be curve C3 as shown in Fig. 7C, where curve C3 is almost the same as cosฦ (curve C1). If 0 deg <ฦ< 90 deg or 90 deg <ฦ< 180 deg, the absolute value of curve C3 is a little smaller than that of curve C1 by about 0.1-1%. If the source of CMB matches the conjugate point C, curve C3 matches curve C1.
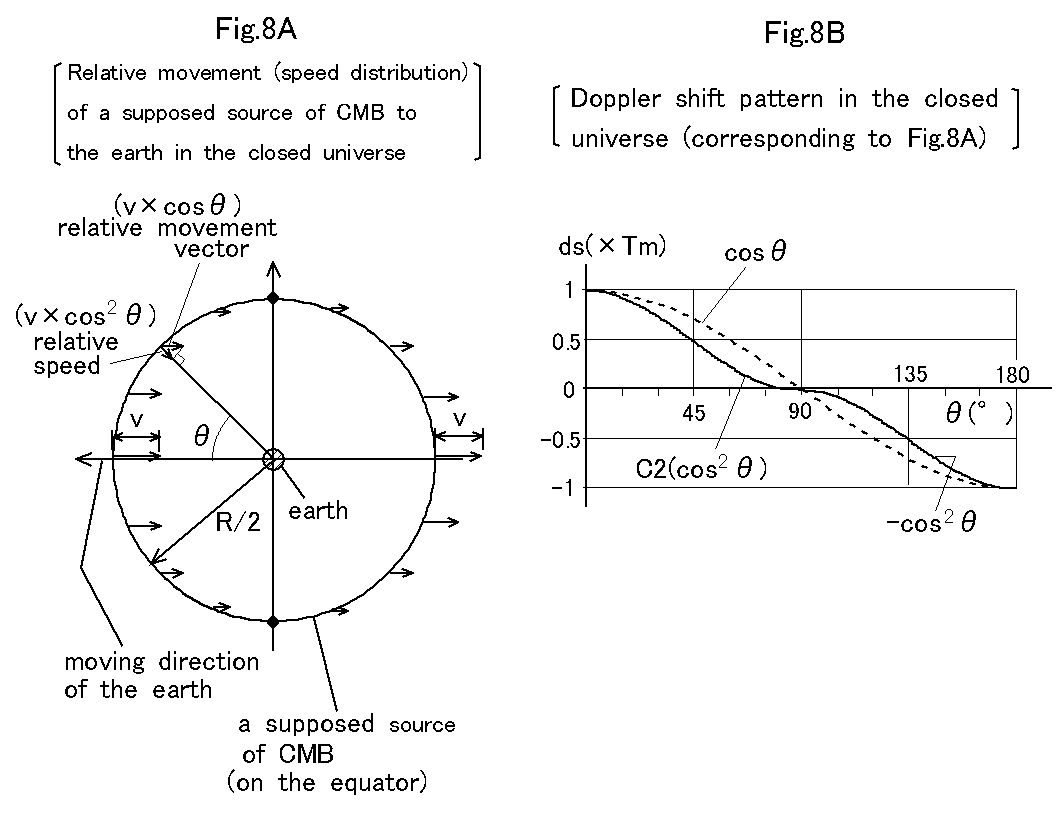
On the other hand if the source of CMB exists on the equator of the closed universe as shown in Fig. 8A, the equivalent source of CMB will match the real source and the relative movement vector of the source to the earth will become cosฦ. And the normalized Doppler shift pattern of the source will be curve C2 as shown in Fig. 8B, where if 0 deg <ฦ< 90 deg, the value of curve C2 is cos2ฦ, and if 90 deg <ฦ< 180 deg, the value of curve C2 is -cos2ฦ. This means that if the position of the source of CMB changes from the equator to the conjugate point C, the normalized Doppler shift pattern of the source will change from curve C2 to curve C1 (see Fig. 7C).
Robot: In short, the Doppler shift pattern of the source of CMB in the closed universe differs a little from that in an open universe (cosฦ pattern), and the Doppler shift pattern of the source of CMB in the closed universe has dipole and low order anisotropies. Further by using the difference between the observed Doppler shift pattern and cosฦ pattern we can calculate radius r of the source of CMB.
CNN reporter: We are everywhere in the solar system. NASA announced that the universe was almost flat. What do you think about it?
Glass Snake: You are very smart. That is the only one and very delicate problem about the closed universe model. First of all, there are the following fundamental questions about the universe:
1. Why is the density of stars so isotropic?
2. Why does the expansion speed of the universe seem to have been accelerated suddenly after about 7 billion years from the Big Bang? Especially why 7 billion years (half of the age of the universe)?
3.
Why is the Z parameter of CMB so isotropic?
Or
why does the expansion speed of the universe seem to be so isotropic when
observed from the earth?
4.
Why does the observed Doppler shift pattern of the source of CMB differ from the expected pattern?
Or
why do the dipole and low order anisotropies of CMB seem to be aligned?
5. Why does the absolute value of the angular correlation function of CMB increase at large angles (about 160-180 deg)?
<<revised>>
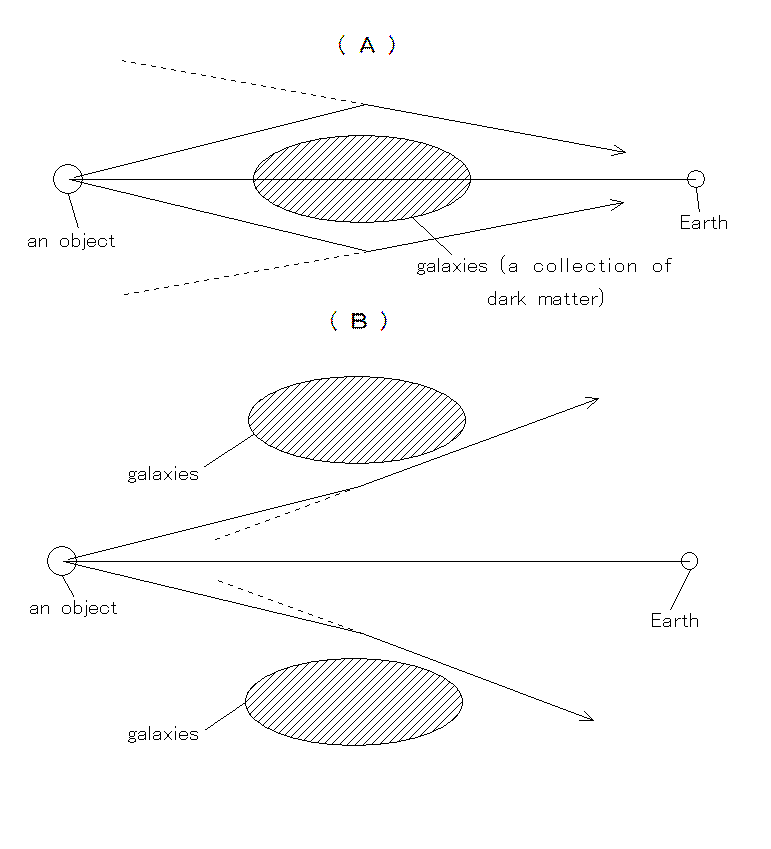
6. Why do all the
so-called gravity lenses have magnification ratio greater than 1 ?
If some galaxies (or a collection of dark matter) exist between an object and the earth as shown in Fig. 81(A), the galaxies act as a lens with magnification ratio greater than 1. On the other hand if other galaxies exist between them as shown in Fig. 81(B), the latter galaxies act as a lens with reduction ration less than 1. When we naturally suppose that all galaxies or dark matter are scattered at random in the universe, the number of gravity lenses with magnification ratio should be nearly the same as the number of those with reduction ratio.
On the contrary all the lenses caused by the spherical effect of the universe have magnification ratio greater than 1.
Fig.81
Then
if we assume that the universe is closed, we can answer all of those questions
quite easily. However if we assume that the flat universe means an open
universe and the universe is open, we cannot answer even one of those questions
easily. It seems to us that we cannot help accepting the closed universe model.
CNN reporter: I like detective novels. Sherlock Holmes once referred to the old axiom:
When all other contingencies fail, whatever remains, however improbable, must be the truth.
You mean that the universe is the largest case?
Glass Snake: Thatfs right. Secondly, although a ray of light in the closed universe travels along a sphere in four-dimensional space, we think that the pass of the ray of light seems to be straight in the conventional three-dimensional world (observable world).
CNN reporter: We will discuss if we report your work to the world at the headquarters.
Robot: The most suitable person to be rewarded is late Edwin Hubble, the spiritual founder of the Gleaners. (Since Edwin Hubble was born in 1889 (the bull year), he is called as Great Bull by the members)
Puzzle Sheep: However, Great Bull would have said
eGood job, members! You have found a little something where other people thought there was noting. But you are a kind of travelers. You have only and merely happened to be in a position where you can see the works of astronomers from an objective point of view. Those to be rewarded are all astronomers, especially the scientists concerned with the projects of measuring CMB. You should go to the next stage based on the closed universe model.f
Robot: In conclusion!
1. The universe is closed. It is the surface of a sphere in (at least) four-dimensional space.
According to the Poincaré conjecture proved by Grigori Perelman, the surface of a sphere in four-dimensional space is similar to a sphere (including inside part) in three-dimensional space. Thus we can exist on (or in) the surface of a sphere in four-dimensional space also from a mathematical point of view.
2. The universe is expanding at the speed of light. In other words the expansion speed of the universe is the speed of light. The universe expands to maintain the space-time relation (distance-time relation). If the expansion of the universe stops, our time will stop.
We
don't necessarily need dark matter or dark energy to explain the structure of
the universe.
3.
The universe is an absolute instrument: all rays of light emitted from any
point of the universe will travel along the passes which converge on its
conjugate point.
4.
The source of CMB is the surface of a sphere whose
center is at the conjugate point of the earth, and the radius of the source is
about from one thousandth to one hundredth of that of the universe.
Glass Snake: In Poincaré conjecture the spherical surface in four dimensional space is similar to
the three dimensional ball, but our world (our spherical surface) is a
four dimensional world, for we can move. We can explain the seeming contradiction
as follows: Because the radius of the spherical surface (universe) is expanding,
namely the universe is a dynamic expanding spherical surface, the fourth
dimension (time dimension) is added to the three dimensions of the ball.
In other words our time is being generated by the expansion of the universe.
Thus our time only passes from the past to the future continuously.
Let's
go to the next stage.
Robot: We should not ask G. Snake what the next stage is.
Glass Snake:
Of course, I know it. Our first job is to eat lunch at the stand-up noodle
shop.
Stamp Pony:
I'm hungry.
Robot:
I shall ask you to close the meeting now.
All:
We are spherical-surfacelings! We are the Gleaners!
Robot:
In Galilei accent!
All:
Buon giorno, we are the Gleaners! And yet it is closed!
Robot:
You, maybe genuine surfacelings! Mission almost accomplished! Dismissed!
Latest update: 2021/09/27
A
mathematical formulation of the closed universe model by the Gleaners (Appendix)(new!)
A narrow and maybe insecure path to the Gleaners:
(Mail to: o-pat-consulting@hotmail.co.jp)