 300 W class low temperature difference Stirling engine
300 W class low temperature difference Stirling engine

 Japanese
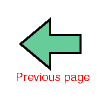
JapaneseThe 300 W class low temperature degree difference Stirling engine is a gamma type Stirling engine and is composed to a displacer, power piston and a heat exchanger. The displacer piston is foamed polyurethane made in order to keep light-weight, and the power piston is aluminum made. Scotch-yoke mechanism is used for driving of a power piston, a side thrust of a piston ring is reduced by this, and then an engine is miniaturized. In a heat exchanger, from upper part, cooler, regenerator, heater is arranged around a displacer cylinder. The heater and the cooler use Finn tubes in order to use hot springs, warm drainage of a plant, as heat-source. The regenerator is a form to pile up a metal net. In order to seal up between engine inside and buffer space, an one-way type piston ring and 1-way type shaft seal is used. By using these devices, the minimum pressure in the engine raises an even buffer pressure level, and it gets possible to increase output of the engine. With this engine, a driving mechanism is covered and sealed up with a shell, and it is possible to add a buffer pressure.
| Engine type | Gamma type | |
|---|---|---|
| Power piston | Bore | 400mm |
| Stroke | 100, 150, 200mm | |
| Material | Alminium | |
| Drive Mechanism | Sckoch Yoke | |
| Displacer Piston | Bore | 800mm |
| Stroke | 80mm | |
| Material | Urethane Form | |
| Drive Mechanism | Simple Crank | |
| Compression Ratio | 1.271 | |
 From being an external combustion engine for Stirling engine, giving and receiving of heat from the outside is done wholly by means of a heat exchanger. A performance of the engine for this reason greatly relies on a performance of a heat exchanger. With a low temperature degree difference Stirling engine, because a heat-source temperature is low, it is necessary to use a heat exchanger of a high performance especially.
From being an external combustion engine for Stirling engine, giving and receiving of heat from the outside is done wholly by means of a heat exchanger. A performance of the engine for this reason greatly relies on a performance of a heat exchanger. With a low temperature degree difference Stirling engine, because a heat-source temperature is low, it is necessary to use a heat exchanger of a high performance especially.With 300 W class low temperature difference Stirling engine, since hot springs or warm drainage of a plant etc. is assumed as heat-source, a heater and cooler use a closs flow type heat exchanger using Finn tube. A regenerator becomes a formality to pile a metal net. From bottom, with an order of a heater regenerator cooler, these are arranged around a displacer cylinder. For a specification of each heat exchanger as follows.
| Heater | Volume | 14866.3 cc |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Fin Tube | |
| Material | Copper | |
| Number of Tubes | 8 | |
| Pitch of Fin | 3.2 mm | |
| Cooler | Volume | 14866.3 cc |
| Type | Fin Tube | |
| Material | Copper | |
| Number of Tubes | 8 | |
| Pitch of Fin | 3.2 mm | |
| Regenerator | Volume | 2424.6 cc |
| Type | Wire Matrix Laminated | |
| Material | Brass Wire Cloth | |
| Mesh | 50 |
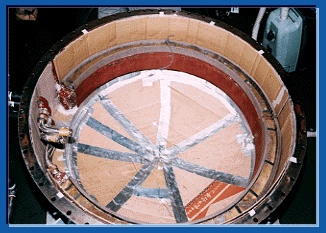
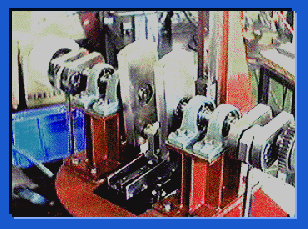 It can say that improvement of a performance of a low temperature difference Stirling engine relies on how it makes a machiniacal loss decrease. Friction of a piston ring occupies a large factor among a machiniacal loss especially. Though it is necessary to make a side thrust (force by a circumference direction of a cylinder added) of a cylinder decrease to make friction of a piston ring decrease, in case that it is used ordinary symple clank mechanism, it is necessary to use very long connecting Rod
It can say that improvement of a performance of a low temperature difference Stirling engine relies on how it makes a machiniacal loss decrease. Friction of a piston ring occupies a large factor among a machiniacal loss especially. Though it is necessary to make a side thrust (force by a circumference direction of a cylinder added) of a cylinder decrease to make friction of a piston ring decrease, in case that it is used ordinary symple clank mechanism, it is necessary to use very long connecting Rod With 300 W class low temperature degree difference Stirling engine, in order to reduce friction of this piston ring, a peculiar Scotch Yoke mechanism is used for driving of a power piston. With this mechanism, linear bearing is arranged rectangularly on Yoke of L shape. A movement of a power piston becomes a sinusoidary straight-line motion by using this mechanism, and a side thrust is greatly reduced and decreased drastically for friction loss of an engine.
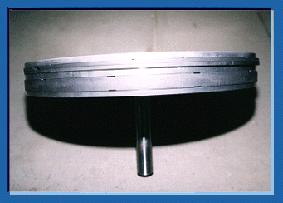 The power piston used for the 300 W class low temperature difference Stirling engine is very large, its bore is 400 mm and siroke is 200 mm. However, a height of this piston is very short with 60 mm level. Since Scotch-yoke mechanism is applied for a driving mechanism of a power piston, don't occur for a neck pretense motion of a piston then, this shape can adopt it.
The power piston used for the 300 W class low temperature difference Stirling engine is very large, its bore is 400 mm and siroke is 200 mm. However, a height of this piston is very short with 60 mm level. Since Scotch-yoke mechanism is applied for a driving mechanism of a power piston, don't occur for a neck pretense motion of a piston then, this shape can adopt it.With piston ring, One-way type piston ring and, rider ring (that is used in order to receive a side thrust) are used. By using the one-way type piston ring, raise the minimum pressure inside an engine even around a buffer pressure and can increase output of an engine.
 For a size of a displacer piston that is used for 300 W class low temperature difference Stirling engine, a height is an about 350 mm with a bore of 800 mm. However, its weight is comparatively light-weight by being foamed polyurethane made. This displacer piston reciprocates inside of cylinder with a stroke of 80 mm by a simple clank mechanism.
For a size of a displacer piston that is used for 300 W class low temperature difference Stirling engine, a height is an about 350 mm with a bore of 800 mm. However, its weight is comparatively light-weight by being foamed polyurethane made. This displacer piston reciprocates inside of cylinder with a stroke of 80 mm by a simple clank mechanism.An important role of a displacer piston is thermal insulation of high-temperature space and low temperature space of an engine and is to make a heat exchanger pass through working gas well. With the displacer of 300 W class low temperature difference Stirling engine for this reason, a simplified piston ring is installed. Working gas, leak from space to space as not passing through a heat exchanger, decreases by this ring. Foamed polyurethane of the material contributes greatly in thermal insulation of both space also.
 Performance of 300 W class low temperature difference Stirling engine
Performance of 300 W class low temperature difference Stirling engine
 300 W class low temperature difference Stirling engine
300 W class low temperature difference Stirling engine
 Return to Stirling Engines of Saitama University
Return to Stirling Engines of Saitama University
 Return to Stirling Engiene Home Page Academic Edition
Return to Stirling Engiene Home Page Academic Edition